Use case at Everis
According to the Spanish law on the Electronic Access of Citizens to Public Services, public administrations must ensure the right of citizens to communicate with them. In the new digital era this implies to provide e-services to promote a more efficient, effective and closer administration. This use case presents a SOA platform developed by Everis in a consortium with other IT companies in order to support this law in the context of the Valencian region government.
The legal framework and requirements must be supported by all of the legal entities (municipalities, small councils) in the area. For enhancing the reusability of the software development, it was decided to create a common infrastructure (the Everis SOA platform) for the whole network of councils in order to share common services. In this way, all of the councils could access to the services offered by the platform, and then they could customize some aspects depending on their needs.
This use case provides a real and challenging environment in which the CDD approach could be tested. First, defining the services to be provided by the platform as capabilities that should reach several goals such as, law requirements or citizens’ satisfaction. These goals must be fulfilled according to the specific context of a wide array of councils, in which the capabilities should be deployed. Secondly, providing KPIs to monitor how effective the service is delivery, and then, providing supporting facts about the improvement of using e-services instead of manual procedures for the public administration. For this use case, three capabilities were redefined using the CDD methodology: a service promotion capability, which dynamically highlight the most relevant services in the main page of council’s website according to context conditions, a registration capability, to provide an electronic way for citizens to enroll and apply for different activities or procedures, and an automatic maintenance capability, to check when services cannot be provide because the infrastructure is in maintenance mode.
Next, we briefly introduce the underlying architecture of this platform. The SOA platform diagram with the different software components related to the capabilities treated in this deliverable is shown in the following figure:
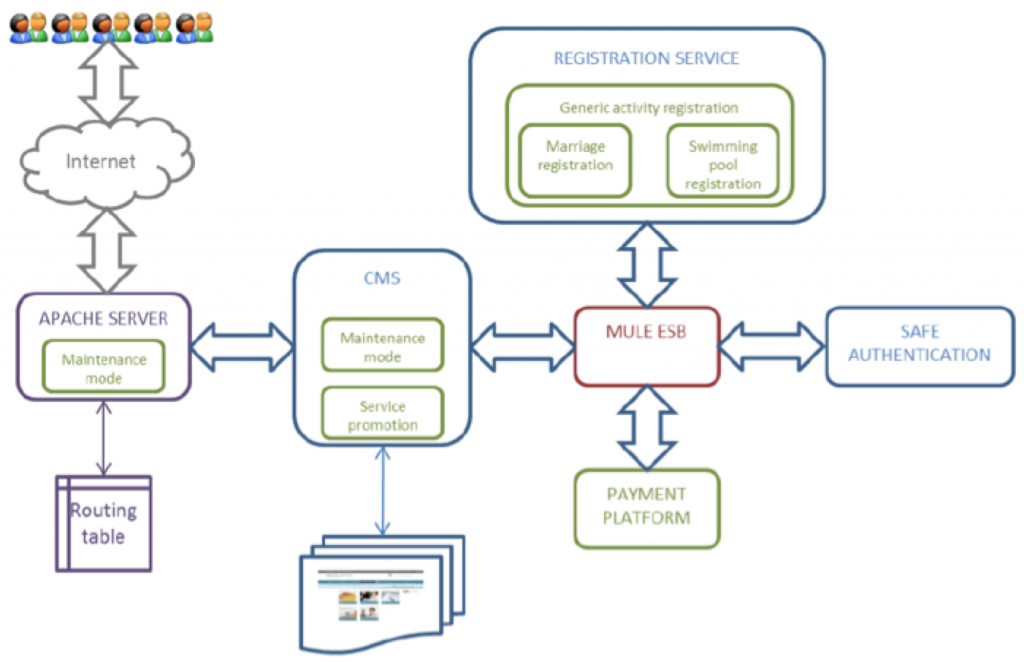
This use case has been supported by
(1) Dynamic Service Registration Capability. The registration service provides an electronic way for citizens to enroll and apply for different activities or procedures. Depending on the procedure, the business process that describes the registration service can change its behavior. There are procedures that require documents, a payment or acceptance by the municipality. This capability has been implemented in two specific processes:
- The swimming pool registration process is a sub process of the general registration process and it starts when the citizen chooses the “Swimming Pool” activity from the catalog of activities. To begin, a list of the pools in the municipality is displayed. The citizen also has the possibility to check for swimming pools in near municipalities and within a desired distance. When a citizen selects a swimming pool, a list of available dates for the selected swimming pool is displayed, including the weather forecast of each date. Once the citizen chooses a desired date, the sub process finishes and the citizen continues with the general registration process.
- The marriage registration process is a sub process of the general registration process and it starts when the citizen chooses the “Marriage” activity from the catalog of activities. To begin, the citizen fills the marriage registration form with personal data about the couple. Then, a list of available dates and hours is displayed, including the weather forecast of each date. Once the citizen chooses a desired date and hour, the sub process finishes and the citizen continues with the general registration process.
(2) Service Promotion Capability. It allows automatical promotion of the most interesting and used services of a municipality’s service catalogue in its home page. If a municipality chooses to have an automatic service promotion ability, then every specified period of time, services are automatically highlighted on the cover of the page. If not, then it is the responsibility of the public servants who manage the municipality’s service catalogue to manually promote services on the cover of the page.
(3) Automatic Maintenance Mode Capability. When, due to context conditions – for instance an infrastructure error, SOA platform cannot provide their services, this platform should enter maintenance mode. In this mode, technical issues detected should be solved before deploying the capability again. The main goal is to assure the capability of providing an automatic maintenance mode of the SOA platform. In this way, when some problem happens, for example CPU or memory problems or incidents with some services, the SOA platform will be able to put itself in maintenance mode automatically.
The capability design and delivery for the automatic maintenance is demonstrated in the video below.
The use case development and execution has led to emergence of patterns describing best practices for eGovernance and Project Management Office. These include patterns on:
- Project Management Office patterns
Support process
Incident reallocation – levels
Incident resolution – plan based
Incident resolution validation
Expertise assurance
Incident resolution plan definition
Automatic maintenance mode
- eGovernance patterns
Support process
Incident reallocation – levels
Incident resolution – plan based
Incident resolution validation
Expertise assurance
Incident resolution plan definition
Automatic maintenance mode
These patterns are document in the Capability Pattern Repository (http://cpr.vitk.lv/search?f[0]=type%3Apartial_capability_pattern&f[1]=field_category%3A273&f[2]=field_category%3A281)